Learn About Different Brain Tumors
As a brain tumor/cancer surgeon and a professor, I have had the privilege to care for patients who were afflicted with brain tumors. Their steadfastness, determination, and optimism serve as inspiration and provide an enhanced perspective of life. You are likely here because you have been diagnosed with a brain tumor or perhaps because you have new neurological symptoms and you are worried. We will focus on the definition, any overall symptoms, and the main tumor types.

What is a Brain Tumor?
Tumors usually form due to changes in DNA of cells resulting in cells that grow erratically into a larger mass. Tumors can arise because of genetic predisposition, environmental exposures, or without a clearly identifiable cause. As the tumor grows in the brain, it can affect brain function by pressure and or irritation due to its size. This will then manifest as symptoms suggestive of increased pressure in the brain as a whole or focal pressure based on location.
Tumors that arise from cells in the brain are called primary brain tumors, whereas those that arise from outside the brain and travel into the brain are referred to as metastatic brain tumors. Tumors can further be categorized as either benign (less aggressive) or malignant (very aggressive). Irrespective of the tumor type, the brain can still be negatively affected by the pressure from the tumor.
Tumors usually form due to changes in the DNA of cells, which results in cells that grow erratically into a larger mass. Tumors can arise because of genetic predisposition, environmental exposures, or without a clear, identifiable cause. As the tumor grows in the brain, it can affect brain function by pressure and or irritation due to its size. This will then manifest as symptoms suggestive of increased pressure in the brain as a whole or focal pressure based on the location.
What are Symptoms of a Brain Tumor?
As previously mentioned, brain tumors generate symptoms that are either generalized or localized, based on the pressure and its location. You may notice these symptoms:
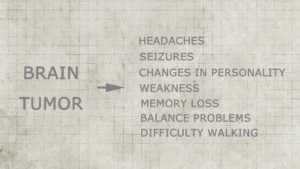
- Headache – Headaches can occur due to increased pressure
- Seizures – Can occur from a brain irritation
- A Change in Personality – Mainly occurs from frontal lobe lesions
- Memory Loss – Can be from frontal and temporal lobe
- Balance Issues – From the cerebellum, parietal, and frontal movement areas
- Fatigue & Weakness
- Difficulty Speaking or Comprehending – your language areas
- Difficulty Walking – your movement areas
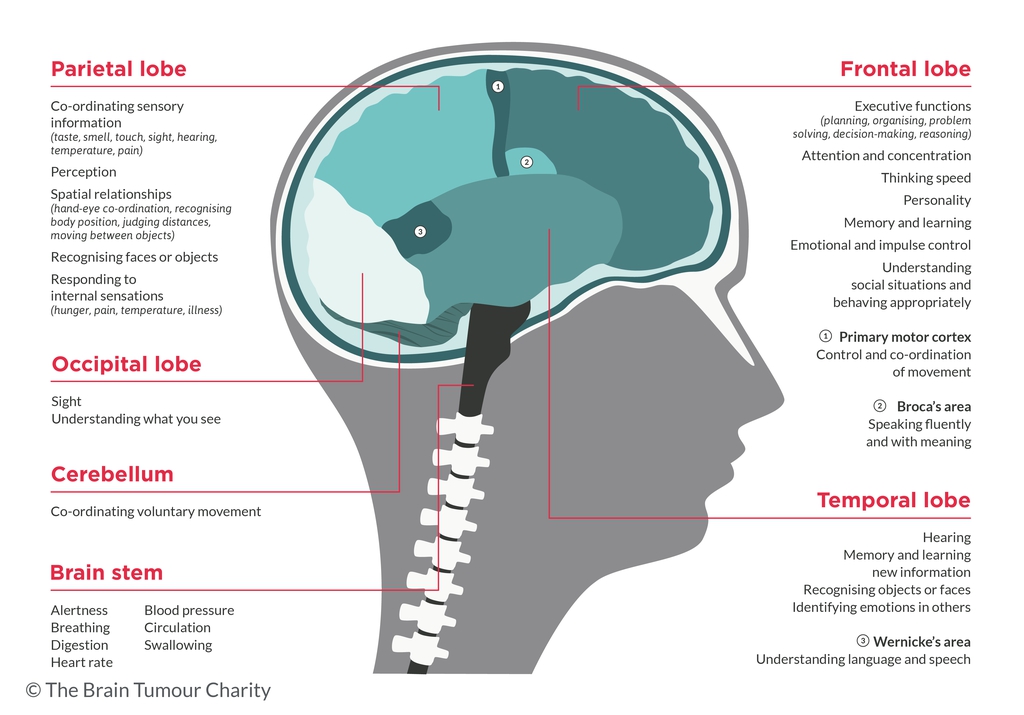
Remember, everyone’s body reacts differently to a brain tumor, and the location of a tumor can produce different symptoms. Here’s a representation (from The Brain Tumour Charity) of the parts of your brain and what they “feel”:
Main Types of Brain Tumors
In 2017, there was an estimate of over 23,000 American adults with a brain tumor and over 3,500 children (from Cancer.net). Here are the main types of brain tumors:
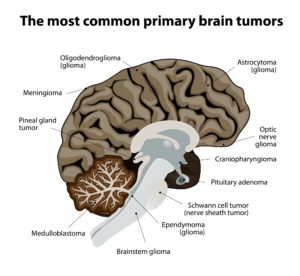
- Cranicpharyngioma
- Glioma
- Astrocytoma
- Brainstem Glioma
- Glioblastoma
- Ependymoma
- Oligodendroglioma
- Optic Nerve Glioma
- Medulloblastoma
- Meningioma
- Pineal Gland Tumor
- Pituitary Adenoma
- Schwann Cell Tumor (Nerve Sheath Tumor)
- Metastatic brain tumors
Glioblastoma is the most aggressive primary brain tumor and deserves a lot of emphases since it is the most common primary brain tumor in adults.
How do doctors know what type of Brain Tumor you have?
Once you present your symptoms and they are suspicious for a tumor, your doctor will order a CT (computed tomography) scan or an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of your brain. This will determine if there is a tumor and where it is located. Both scans can share a lot of information with your physician. The MRI is known to provide your doctor with more details about your brain compared to a CT scan. The MRI characteristics coupled with the number of tumors seen can provide clues as to whether the tumor is a primary brain tumor versus a metastatic brain tumor. One could also decipher if the tumor is malignant or benign. Sometimes the MRI can provide clues if the mass is seen actually as an abscess as opposed to a tumor. Ultimately, the diagnosis is attained through a biopsy or actual removal of the tumor followed by an examination of the specimen by a pathologist.
If you would like to learn about the classification of a multitude of different types of brain and nervous system tumors, please read the information from an article in the Acta Neuropathologica, “The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary.”